MAULANA ABUL KALAM AZAD UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, WEST BENGAL
MBA PROGRAMME
(Revised Curriculum – 2018)
Objective
To conduct business and industry – oriented MBA Programme following AICTE Model Curriculum for Management (MBA & PGDM), 2018.
Course
- Two – Year full-time MBA course (Four – Semester).
- Minimum number of class room contact teaching for MBA/PGDM programme should be 96 credits (one credit equals 10 hours) and Internship / Project should be 06 credits i.e., Total 96 + 06 = 102 credits.
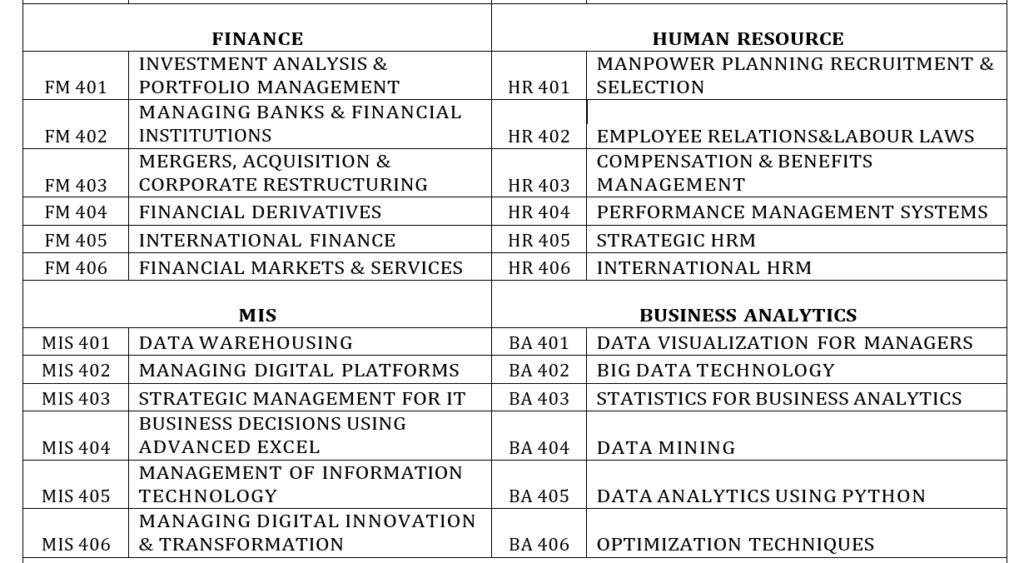
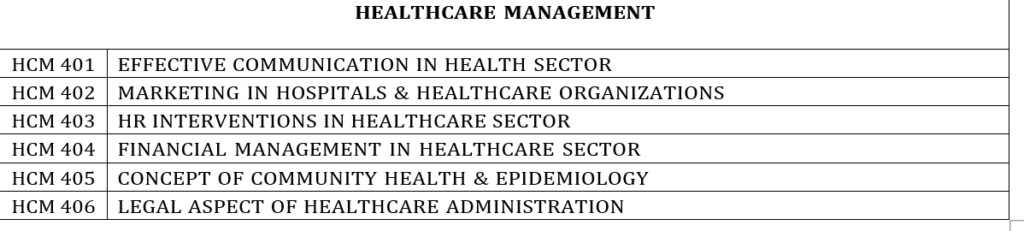
- Specialization: Students can opt for any two functional specializations (One Major Area and one Minor Area) from Marketing, Finance, HRM, Operations Management, Healthcare Management, MIS and Business Analytics
- Each Paper = 4 credits (40 contact hours), 6 Papers / Semester
- Marks per paper: 100 (70 – University, 30 – College)
Course Structure
- Regular Course
| Semester | Paper | Credit (1=4 credit) | Contact Hrs. (1 = 10 hrs.) |
| I (C*) | 6 | 24 | 240 |
| II (C*) | 6 | 24 | 240 |
| III (2 C*+4 E**) | 6 | 24 | 240 |
| Internship/Project # | 2 | 6 | 60 |
| IV (6 E**) | 6 | 24 | 240 |
| Course Total | 26 | 102 | 1020 |
(# Project: Project Paper + Presentation + Viva) (C*: CORE PAPERS/E**: ELECTIVE PAPERS)
- On – Line Courses (Non-credit, Paper & Marks to be mentioned in the Mark sheet)
- Total : 4(1/Semester)
- Weightage : 4 Credits / Paper = 04 X 4 = 16 credits
- Courses (any 4): Environment Sciences, Indian Society & Culture, Indian Constitution, Entrepreneurship, English Communication, Data Mining, E-Commerce, Agri-Business, Hospitality Management, Small Business Management, Corporate Social Responsibility.
| Total Credits: | |
| Regular : | 102 |
| On-Line (Non-Credit) : | 16 |
Session
- July – December (Odd Semesters / 1st& 3rd)
- January – June (Even semesters / 2nd& 4th)
- Class / Day : 5 hrs / Day (5 days week)
- Project Work : after 2ndSem Examination, June & July (8 Weeks)
Examination System (Semester – Wise)
- Total Marks = 100 (University – 70, College – 30)
- Internal (College level) : Weightage : 30 (20-Class Test, 10-Presentation & Viva)
- Paperwise Class Test = 2 Tests / every Six weeks
- Average of 2 internal tests (2 components – Test, Presentation& Viva)
- External (University Level) : 70 (20 = MCQ, 20 = Short Q, 30 = Analytical Q and Cases)
- Semester Grade Point Average : SGPA
- Yearly Grade Point Average: YGPA
- Degree Grade Point Average : DGPA
- Odd Semester (1st& 3rd) Examination : 1st Week of December
- Even Semester (2nd& 4th) Examination : 1st Week of May
- Project Marks (100) : Project Report (50), Presentation (30), Viva (20)
- Passmarks : 40 per paper, 50% aggregate
Teaching Methodology
Lecture, Discussion, Presentation, Case Studies, Group Task, Assignments, Projects, Special Lectures by industry professionals.
Internship / Project
Six to Eight weeks Internship Project in industry. Students will be required to submit a Project Report on any area of Elective courses (Finance, Marketing, HRM, Operations Management, Business Analytics, MIS, Healthcare Management) under the Faculty guidance. The Project will be examined on Project Report, Presentation and Viva.
General Guidelines
- This MBA curriculum will be applicable from the academic year 2018 – 19.
- All rules and regulations regarding admission, examination, registration, migration and others shall be according to MAKAUT norms.
Core Courses (Six / Semester)
CURRICULUM
Semester – I
MB – 101 Managerial Economics (Micro) MB – 102 Organizational Behaviour
MB – 103 Business Communication
MB – 104 Legal and Business Environment (Micro and Macro) MB – 105 Indian Ethos and Business Ethics
MB – 106 Quantitative Techniques
Semester – II
MB – 201 Indian Economy and Policy
MB – 202 Financial Reporting, Statements and Analysis MB – 203 Marketing Management
MB – 204 Operations Management
MB – 205 Management Information System MB – 206 Human Resource Management
Semester – III Core Papers:
MB – 301 Entrepreneurship and Project Management MB – 302 Corporate Strategy
Elective Papers: Two from any one Functional Area (Major) and two from a different Functional Area (Minor)
FM/ MM/HR/OM/BA/ MIS/ HCM– 301 FM/ MM/HR/OM/BA/ MIS/ HCM – 302 FM/ MM/HR/OM/BA/ MIS/ HCM – 303 FM/ MM/HR/OM/BA/ MIS/ HCM – 304
MB – 303 Internship Project and Viva Voce
Semester – IV
Elective Papers (Four from Major Functional Area and Two from Minor Functional area) **
FM/ MM/HR/OM/BA/ MIS/ HCM – 401
FM/ MM/HR/OM/BA/ MIS/ HCM – 402 FM/ MM/HR/OM/BA/ MIS/ HCM – 403 FM/ MM/HR/OM/BA/ MIS/ HCM – 404 FM/ MM/HR/OM/BA/ MIS/ HCM – 405 FM/ MM/HR/OM/BA/ MIS/ HCM – 406
**The Major and Minor Functional areas will be same as chosen in the 3rd Semester.

FIRST SEMESTER
MODULE I
MB 101: MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS (MICRO)
- Introduction to Managerial Economics [2L]
- Basic problems of an economic system
- Goals of managerial decision making
- Resource allocation using PPC
- Demand Analysis [10 L]
- Demand Functions – Law of Demand, Explaining the law of demand, Violations of the Law of Demand, Shifts in Demand; Elasticity of Demand: Price Elasticity (at a point and over and interval), Factors affecting price elasticity, Price elasticity and Change in Total Revenue, AR, MR and Price elasticity, Range of Values of Price Elasticity; Income Elasticity, Inferior, Superior and Normal goods, Income Elasticity and Share in Total Expenditure; Cross-Price Elasticity, Substitutes and Complements
- Indifference curves, budget line and consumer equilibrium
- Introduction to methods of demand estimation (concepts only)
- Production and Cost Analysis [14L]
- Production Function, Short Run and Long Run, Production with One Variable Input, Total Product, Average and Marginal Products, Law of Variable proportions, Relationship between TP, AP and MP.
- Short Run Costs of Production, Fixed and Variable Costs, Short Run Total, Average and Marginal Cost and Relationship between them, Short Run Cost Curves, Relationship between AVC, MC, AP and MP; Long run cost curves, Relationship between LAC and SAC, Economies of Scale and Scope.
- Production with Two Variable Inputs, Isoquants – Characteristics, Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution, Laws of Returns to Scale, Isocost Curves, * # Finding the Optimal Combination of Inputs, Production of a given output at Minimum Cost, Production of Maximum Output with a given level of Cost, Expansion Path, Finding the Long Run Cost Schedules from the Production Function,
- Law of supply, elasticity of supply, market equilibrium, changes in equilibrium.
MODULE II
- Alternate Goals of Managerial Firms [2 L]
- Profit maximization
- Revenue maximization
- Managerial utility maximization
- Managerial Decision Making under Alternative Market Structures [6 L]
- Characteristics of Perfect Competition, #Profit Maximization in Competitive Markets, Output Decision in the Short Run, Shut Down Point, Short Run Supply for the Firm and Industry; Output Decision in the Long Run, Break Even Point, Long Run Supply for the Perfectly Competitive Industry
- Price and output decision under different market structure – Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition, Oligopoly – cartel, price leadership.
- Pricing Decisions [6 L]
- Price Discrimination under Monopoly, Transfer Pricing.
- Market Failure
- Game theory &Asymmetric information
Suggested Readings:
- Damodaran, Suma – Managerial Economics – Oxford University Press
- Lipsey & Chrystal – Economics – Oxford University Press
- Peterson & Lewis – Managerial Economics – Pearson Education.
- Pindyck and Rubenfeld – Micro Economics – Pearson Education
- H.L. Ahuza- Managerial Economics, S. Chand
- D.N. Dwivedi- Managerial Economics, Prentice Hall.
MODULE I
MB 102: ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOUR
- OB – Overview – Meaning of OB, Importance of OB, Field of OB, Contributing Disciplines, Applications in Industry. [2L]
MAKAUT/MBA/1ST SEM
(4 Credit: 40 hrs)
- Personality– Meaning of Personality, Determinants of Personality, Theories of Personality, Measurement of Personality, Development of Personality [6L]
- Perception – Process and Principles, Nature and Importance, Factors Influencing, Perception, Perceptual Selectivity, Social Perception, Fundamentals of Decision making.
[4 L]
- Work Motivation – Approaches to Work Motivation, Theories of Motivation – Maslow’s Hierarchy of Need Theory, Alderfer’s ERG Theory, Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory, McClelland’s Achievement – Motivation Theory, McGregor’s Theory X & Y, Vroom’s Expectancy Theory, Porter Lawler Expectancy Model [6L]
- Attitudes and Job Satisfaction – Sources of Attitudes, Types of Attitudes, Attitudes and Consistency, Cognitive Dissonance Theory, Attitude Surveys. [2L]
MODULE –II
- Organization – Mission, Goals, Characteristics, Types, Organizational Theory- Classical Theories: Scientific Management, Administrative Principals, Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach, Modern Theories: System Approach, Contingency Approach, Quantitative Approach, Behavioral Approach, Managing Organizational Culture. [6L]
- Group Behavior – Characteristics of Group, Types of Groups, Stages of Development,
Group Decision-making, difference work group and work team, Why work Teams, Work team in Organization, Team Building, Organizational Politics. [4L]
- Leadership – Leadership Theories, Leadership Styles, Skills and influence process, Leadership and power, Examples of Effective Organizational Leadership in India, Cases on Leadership, Success stories of today’s Global and Indian leaders. [4L]
- Conflict in Organization – Sources of Conflict, Types of Conflict, Conflict Process, Johari Window, Conflict Resolution, Cases on Conflict Resolution. [2L]
- Organizational Change – Meaning and Nature of Organizational Change, Types of Organizational Change, Forces that acts as stimulant to change. Resistance to change, How to overcome resistance to change, Approaches to managing Organizational Change, Kurt Lewin’s three Step model, Action research model, Kotter’s eight step model.
[4L]
Suggested Readings:
MAKAUT/MBA/1ST SEM
(4 Credit: 40 hrs)
- Robbins, S.P. Judge, T.A. & Sanghi, S.: Organizational Behaviour, Pearson
- Luthans, Fred: Organizational Behaviour, McGraw Hill
- Newstrom J.W. &Devis K.: Organizational Behaviour, McGraw Hill
- Aswathappa ,K : Organisational Behaviour ,Himalaya Publishing House
- Shukla, Madhukar : Understanding Organizations – Organizational Theory & Practice in India, Prentice Hall
- Sekharan, Uma: Organisational Behaviour , The Mc Graw –Hill Companies
Module I:
MB 103: BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
- Principles of Communication – Definition, Purposes, Types, Process, Models and Barriers [2L]
- Verbal and Non Verbal Communication – Presentation Skills (Planning and Preparation/ Using Visual Aids/ Delivery), Individual and Team Presentations, Public Speaking, Listening and Feedback, Body Language [4L+6 P]
- Written Communication – Stages of Writing, Composing Business Messages, Preparing Notes, Style, Punctuation, Using simple words, Proof Reading. [ 4L]
- Report Writing – Report Planning, Types of Reports, Developing an outline, Nature of Headings, Ordering of Points, Logical Sequencing, Graphs, Charts, Executive Summary, List of Illustration, Report Writing. [4L]
Module II:
- Internal Communication – Circulars, Notices, Memos, Agenda and Minutes [4L + 2P]
- External Communication – Resume/CV, Using Facsimiles (Fax), Electronic Main, Handling Mail [4 L]
- Writing Business Letters – Formats, Styles Types – Request, Enquiry, Placing Order, Instruction, Action, Complaint, Adjustment, Sales, Reference, Good News & Bad News, Acknowledgement [2L + 4P]
- Handling Business Information – Annual Report, House Magazine, Press Release, Press Report [2 L + 2P]
Suggested Readings:
- Monipally: Business Communication, Tata McGraw Hill
- Business Communication Essentials (6th Edition) by Courtland L. Bovee & John V. Thill, Pearson
- Business English: A Complete Guide for All Business and Professional Communications by Prem P. Bhalla; UBS Publishers
- The Effective Presentation: Talk your way to success by Asha Kaul; SAGE
- Madhukar: Business Communications; Vikas Publishing House
- Senguin J: Business Communication; Allied Publishers
MB 104: LEGAL AND BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT (MICRO & MACRO)
Module I: Legal Environment
- Legal Aspects of Business – Society, State and Law, Enforceability of Law, Mercantile Law. [2L]
- Indian Contract Act, 1872 – Contract defined, Elements of valid contract, Classification of contracts, Offer and acceptance, Consideration, Capacity to contracts, Free consent, Legality of object and consideration, Illegal agreements, Termination of contracts, Breach of contract, Indemnity and guarantee, Laws of agency [6L]
- Sale of Goods Act, 1930 – Classification of goods, Conditions & Warranties, Passing of ownership rights, Rights of an unpaid seller, Remedies for breach of Contract of Sale of Goods. [4L]
- Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 – Definition and characteristics of different types of negotiable instruments, Parties to a negotiable instrument and their capacity, Dishonour of cheques, Discharge from Liability, Crossing of cheques, Bank drafts and Banker’s cheques. [4L]
- Companies Act, 1956 – Nature and kinds of companies, Formation, Memorandum, Articles, Prospectus, Capital – shares, debentures, borrowing powers, minimum subscription, Appointment of Directors; Winding up of companies (Including Amendments) [6L]
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986 – Salient features and objectives of the Consumer Protection Act, 1986, Different Consumer redressal Forums, Composition and jurisdiction of district, state and National forum, Mode of complaints, Procedures for disposal of complaints, Penalty. [4L]
- Intellectual Property Right– Laws relating to Patents (Patent Act, 1970), Trademarks (Trademark Act, 1999), Copyright (Copyright Act, 1957), Geographical Indications (Registration & Protection) Act, 1999 [4L]
Module II: Business Environment
- Economic Indicators – Consumer Price Index, Interest Rate, Inflation Rate and its impact on Business, Business Risk [4L]
- Intellectual Property Regime (WTO Guidelines) [2L]
- Legislation for Anti competitive and Unfair Trade Practice – Objectives of MRTP Act, 1969, Objectives of Competition Act, 2002, Monopolistic Trade Practice, Anti competitive Agreement, MRTP vs Competition Act [4L]
Suggested Readings:
- Sen & Mitra: Commercial law; World Press
- Pathak: Legal Aspect of Business, TMH
- Das & Ghosh: Business Regulatory Framework: Ocean Publication, Delhi
- Pillai & Bagavathi: Business law, S. Chand
- Dutt & Sundaram: Economic Environment of Business, S. Chand
- Misra, S. K & Puri, D. K.: Economic Environment of Business, Himalaya Publishing
MB 105: INDIAN ETHOS AND BUSINESS ETHICS
Module – I: Indian Ethos
- History & Relevance; Principles, practiced by Indian Companies; Role of Indian Ethos (Management lessons from Vedas, Mahabharata, Bible, Quran, Arthashastra,) Indian Heritage in Business. Ethics Vs Ethos, Indian Vs Western Management; Work ethos and values for Indian Managers [6L]
- Relevance of Value-based Management in Global change- – impact of Values on stake holders; Trans-cultural human values ; Secular – Vs Spiritual values; value system in work culture [4 L]
MAKAUT/MBA/1ST SEM
(4 Credit: 40 hrs)
- Stress Management, – meditation for mental health, yoga [2 L]
- Contemporary Approaches to Leadership – Joint Hindu Family business; Leadership qualities of Karta [2 L]
- Indian systems of learning– Gurukul system of learning, advantages – disadvantages of Karma, Importance of Karma to managers , Nishkama Karma- laws of Karma ; Law of creation- Law of humility- Law of growth – Law of Responsibility- Law of connection – Corporate Karma Leadership [6 L]
Module – II: Business Ethics
- Understanding Business Ethics – Ethical Values, Myths and Ambiguity, Ethical Codes, Ethical Principles in Business; Theories of Ethics, Absolutism vs. Relativism [6 L]
- Approaches to Business Ethics: Teleological Approach, The Deontological Approach , Kohlberg’s Six Stages Of Moral Development (CMD) [4 L]
- Managing Ethical Dilemma: Characteristics, Ethical Decision Making, Ethical Reasoning, The Dilemma Resolution Process; Ethical Dilemmas In Different Business Areas Of Finance, Marketing, HRM and International Business [4 L]
- Ethical Culture in Organizations – Developing Code of Culture in Organization, Ethical and Value-Based Leadership. Role of Scriptures in Understanding Ethics, Ethics in Business, Strategies of Organizational Culture Building, Ethical Indian Wisdom and Indian Approaches towards Business Ethics. [6 L]
Suggested Readings
- Beteille, Andre – Society and Politics in India, OUP
- Chakraborty, S. K. – Values and Ethics for Organisations, OUP
- Fernando, A.C. – Business Ethics – An Indian Perspective, Pearson
- Gupta, Dipankar – Social Stratificaiton, OUP.
- Srinivas, M. N.- Social Structure and Caste and Other Essays, OUP.
- Sandhya, N- Indian Society, Vrindya Publication
MB 106: QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES
Module I:
- Linear Programming: Formulating maximization/minimization problems, Graphical solution, Simplex method, Artificial Variables – Big M – Method, Special cases of LP, Duality of LP and its interpretation, Post Optimality/Sensitivity Analysis, Applications of LP. [6L]
- Transportation Problems: Introduction – Mathematical formulation of transportation problem – the Transportation method for finding initial solutions-North West Corner Method – Least Cost Method – Vogel’s Approximation method – test for optimality – steps of MODI method-loops in transportation table – Degeneracy. [6L]
- Assignment Problems: Introduction – Mathematical statement of the problem-Hungarian method of solution – Maximization case in assignment problem—unbalanced assignment problem – restrictions on assignment – Travelling salesman problem. [4L]
- Theory of Games: Introduction – Two person zero sum games – Pure strategies – games with saddle points – rules to determine saddle points – mixed strategies – Game without saddle points – the rules of dominance – Methods of solution for games without saddle points—algebraic methods, graphical methods. [4L]
Module II:
- Basic Statistics: Basic Concept (Variables, Population v/s Sample, Central tendency, Dispersion, data Visualization, Simple Correlation and Regression. [4L]
- Probability & Distribution: Probability – Introduction, Rules of Probability, Conditional Probability (Baye’s Theorem), Random Variables, Discrete and Continuous Distributions (Binomial, Poisson and Normal), Sampling – Types and Distribution. [6L]
- Theory of Estimation: Estimation – estimation problems, standard error, margin of error, confidence error, confidence interval, characteristics of estimators, consistency unbiasedness, sufficiency and efficiency, most sufficient estimators. Point Estimation and Interval Estimation. [4L]
- Statistical Inference: Hypothesis Testing, Parametric Test – Z, F, t test, ANOVA, Non Parametric Test – Chi square test (goodness of fit, independence of attributes) Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient. [6L]
Software Packages to be used in illustrating the above methods
Suggested Readings
- Statistics by Wayne L. Winston
- Business Statistics by GC Berry
- Business Statistics, Problems & Solutions by JK Sharma
- Operations Research by A Ravindran, Don T Philips and James J Solberg..
- Operations Research by V K Kapoor
Operations Research by S K Kalavathy
SECOND SEMESTER
MODULE I
MB 201: INDIAN ECONOMY AND POLICY
1. Circular Flow of Income
National Income Accounting –terms and concepts, three methods of measuring GDP/GNP (3L)
2. Theory of Income Determination
Simple Keynesian model: Aggregate demand – Aggregate supply method, Savings- investment method
Concepts of multiplier: Autonomous expenditure multiplier, introducing the Government, Government expenditure multiplier, Tax Rate Multiplier, Balanced Budget Multiplier, Open economy – Export and import multipliers.
| Paradox of Thrift, Crowding out effect, Business cycle – phases and stabilization | (6L) |
| 3. Introduction of Money and Asset Market IS-LM model, Fiscal policy and monetary policy using IS-LM | (4L) |
| 4. Inflation and Unemployment | |
| Concepts of inflation – demand pull and cost push, Stabilization policies | |
| Introduction to Philips curve as relation between inflation and unemployment. | (3L) |
| 5. Introduction to Foreign Trade & International Linkages | |
| Concepts of Balance of Payments | |
| Alternative exchange rate systems – fixed, flexible and managed float | |
| Comparative Advantage as basis for trade; | |
| Tariff and non-tariff barriers | (4L) |
| MODULE II 6. Indian Economy – An Overview | |
| Evolution of Indian economy since independence | |
| Liberalization of Indian economy since 1991 | (4L) |
| 7. New Industrial Policy LPG model, New Industrial Policy (1991) | (4L) |
8. Banking and Capital Market Reforms
Banking structure in India, Composition of Indian Capital market,
SEBI and Capital Market Reforms (4L)
- Monetary and Fiscal Policy Reforms Composition of Indian money market Components and Instruments of Monetary policy
Concepts and Management of Deficits (4L)
10. Trade Policy Reforms
Major components of trade policy reforms Idea of FEMA, NITI AYOG role and function
Current and capital account convertibility. (4L)
Suggested Readings:
- Principles of Macroeconomics – SoumyenSikdar, (OUP)
- Managerial Economics – Suma Damodaran, (OUP)
- Macroeconomics – Dornbusch , Fischer &Startz (PHI)
- Economic Environment of Business: S.K. Mishra and V.K. Puri,
- Indian Economy: Datt & Sundharam,
- Indian Economy since Independence, Uma Kapilaed.
MB 202: FINANCIAL REPORTING, STATEMENT AND ANALYSIS
MODULE I
- Basic Financial Accounting Concept: Meaning and Scope of Accounting –Definition of accounting-classification of accounting- GAAP- Accounting Concepts and Conventions –Accounting Equation (2L)
- Preparation Of Books Of Accounts: Event-Transaction- Accounting Cycle – Golden Rule- Journal-Ledger-Trial Balance-Final Account (10L)
- Basic Cost Accounting Concept- Cost Concept-Cost Unit- Technique of Costing- Method of Costing- Cost center- Cost Unit- Cost Sheet preparation and Interpretation. (4L)
- Introduction to Accounting Standard: Introduction to Indian GAAP and IndAS- Introduction to IFRS and IAS- Comparative Analysis of Indian GAAP and IndAS. (4L)
MODULE II
- Preparation Of Financial Statement: Trading Account-Profit & Loss Account – Balance Sheet (As per Schedule VI, old & new) with Adjustment Entries – Preparation and Interpretation of Annual Report -Corporate Social Responsibility – Human Resource Accounting-Value Added Statement (10L)
- Financial Statement Analysis: Comparative Statement- Common Size Statement- Trend Analysis- Ratio Analysis–Fund Flow Statement – Cash Flow Statement. (10L)
Suggested Readings:
- M. Hanif & A. Mukherjee : Financial Accounting. McGraw Hill
- S. K. Paul: Financial Accounting, New Central book Agency
- S. P. Jain & K. L. Narang: Cost and Management Accounting. Kalyani Publication
- P. M. Rao: Financial Statement Analysis and Reporting. PHI
- T. P. Ghosh, N. Ankarnath, K. J. Mehta & Y. A. Alkafazi: Understanding IFRS Fundamentals, Wiley
- Tulsian & Tulsian: Corporate Financial Reporting, S. Chand
MB 203: MARKETING MANAGEMENT
MODULE I
- Introduction: Definitions of marketing; Core Concept of Marketing – need, want, demand, offering and branding, value and satisfaction, Evolution of marketing concepts (orientations); Marketing Mix – 4Ps and 4Cs. [2 L]
- Marketing Environment: Major components of Internal Environment, the micro- environment and macro-environment; SWOT Analysis, PEST Analysis [2 L]
- Strategy and Planning: Concept of SBU, Choice of Corporate level Strategy; BCG matrix, Product-Market Grid, Porter’s Five Force Model for Industry Analysis. [4 L]
- Market Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning (STP): Concepts of market segmentation: Various bases for segmentation: Geographic, Demographic, Psychographic (VALS-II) and Behavioural; Targeting: Mass marketing, Segment Marketing, Niche Marketing, Micro Marketing and Customization; Concept of Differentiation and Positioning. [4 L]
- Consumer Behaviour and Marketing Research: A framework of consumer decision making process, overview of major factors influencing consumer behavior; marketing research: Role in decision making, Steps and process of Marketing Research, B2B Marketing. [4 L]
MODULE II
- Product: Product Classification, Service – characteristics and expanded service mix elements; Product Levels, Product Mix, Product Line Management, Product Life Cycle: concept and types, New Product Development. [6 L]
- Branding and Packaging: Purpose of branding; Brand equity; Branding strategies; Purpose of Packaging; Types of Packaging – primary, secondary, shipping packages.
[3 L]
- Pricing: Procedure for price setting; Pricing objectives; Cost and Demand consideration; Pricing Methods, Pricing Strategies [3 L]
- Marketing Channels: Channel flows and functions; Channel design decisions; Wholesaling and Retailing, Concept of Supply Chain Management and Logistics Management, Channel Conflict Management [5 L]
- Promotion: Elements of Promotion Mix (Advertising, Sales Promotion, Personal Selling, Direct Marketing, Publicity & PR), 5M model of Advertising, Concept of Digital Marketing; Overview of Selling Process [5 L]
- Basic concepts of market potential: Sales potential/ Market Share and Sales forecast; Methods of Sales forecasting. [2 L]
Suggested Reading:
- Kotler, P., Keller, K., Koshy, A. & Jha, M. – Marketing Management; Pearson
- Ramaswamy & Namakumari – Marketing Management; McMillan
- Saxena, R. – Marketing Management; TMH
- Kurtz, David L, Boone , Louis E – Principles of Marketing; Thomson
- Keith Blois – Text Book of Marketing; Oxford University Press
- Etzel, M.J., Walker, B.W. & W.J. Stanton – Marketing; TMH
MB 204: OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
MODULE I
- Introduction to Production and Operations Management: Difference between Manufacturing and Service Operations; Product Process Matrix capacity planning- Responsibilities of Production Manager; Production as a Coordination Function; Production Cycle, Production Planning & Control Concept. (4L)
- Characteristics of Manufacturing Systems: Classification of Manufacturing Systems with Examples; Differences between Intermittent and Continuous Production (2L)
- Plant Location: Need for a Good Plant Location; Factors influencing Plant Location – Tangible and Intangible Factors; Economic Survey of Site Selection (2L)
- Plant Layout: Need for a Good Plant Layout; Characteristics of a Good Layout; Costs associated with Plant Layout; Process Layout vs. Product Layout; Optimization in a Process Layout and Product Layout; Designing Product and Process Layout; Assembly Line Balancing – Concept and Problems; Cellular Manufacturing Concept (6L)
- Maintenance Management: Types of Maintenance – Breakdown and Preventive Maintenance; Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) (3L)
MODULE II
- Purchase Management: Purchasing Procedure; Value Analysis; Vendor Selection; Negotiation; Make or Buy decision (2L)
- Inventory Management: Classification of inventory items – ABC, FSN, VED classification; Introduction to EOQ and EBQ; MRP – Concept, inputs and outputs, benefits, examples; Deterministic demand model–EOQ- Continuous and Periodic review Inventory models; Master Production Schedule and MRP; Concepts of MRP II, JIT and ERP (6L)
- Inspection & Quality Control: Types of Inspection; Statistical Quality Control – Acceptance Sampling and Control Charts (5L)
- Scheduling: Sequencing – Definition and Assumptions; Sequencing of n jobs on a single machine – Shortest Processing Time, Longest Processing Time, Earliest Due Date and First Come First Serve basis; Sequencing of 2 jobs on 2 machines – Gantt Charts, Limitations of Gantt Charts; Sequencing of n jobs on 2 and 3 machines – Johnson’s Rule; Introduction to Project Management – CPM and PERT, Identification and Importance of the Critical Path (6L)
- Work Study: Definition and its Importance; Basic Procedure in Performing a Work Study; Method Study –Objectives and Procedure; Work Measurement–Objectives and Procedure; Concepts of Performance Rating, Basic Time, Allowances and Standard Time (4L)
Suggested Readings:
- Chary, S.N. – Production and Operations Management; TMH
- Panneerselvam, R. – Production and Operations Management, PHI
- Bedi, K. – Production and Operations Management; Oxford University Press
- Chase, Jacobs, Aquilano and Agarwal – Operations Management for Competitive Advantage; TMH
- Buffa, E. S. and Sarin, R.K. – Modern Production / Operations Management; John Wiley
- Collier, Evans and Ganguly – Operations Management; Cengage Learning
MB 205: MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM
MODULE I
- E-commerce / E-business [3L]
Overview, Definitions, Advantages & Disadvantages of E-commerce
Business models of e-commerce: models based on transaction party (B2B, B2C, B2G, C2B, C2C, E-Governance), models based on revenue models
Implementation ecommerce business, online and offline marketing
2. ERP, CRM, SCM [10L]
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning):
Concepts of ERP, architecture of ERP, Generic modules of ERP, Applications of ERP, concept of XRP (extended ERP)
Features of commercial software like SAP, Oracle Apps, MS Dynamics NAV CRM (Customer Relationship Management):
Concepts of CRM, Features, application of CRM Sales force automation
SCM (Supply Chain Management):
Concepts of SCM, drivers of SCM, inbound & outbound
Definition, brief description and applicability of: eProcurement, eTailing, eLogistics, eCollaboration, eIntegration.
Case studies for ERP, CRM, and SCM
- Data Communication & Networking [4L] Need for computer networking, components of a data communication system, Network topology
Types of networks: LAN, MAN, WAN; concepts of Internet, Intranet, Extranet, and WWW.
Network protocols, Network Architecture
MODULE II
- Threats to Computer Systems and Control Measures [2L] Concepts of threats: Virus, hacking, phishing, spyware, spam, physical threats (fire, flood, earthquake, vandalism)
Concepts of security measures: firewall, encryption
5. Database Management Systems (DBMS) [e.g. MS-Access/ Oracle/ MS SQL Server
/ MySQL etc.] [4L+2P]
What is a DBMS; Need for using DBMS. Concepts of tables, records, attributes, keys, integrity constraints
SQL: DDL & DML, DCL concepts, SQL commands [ANSI standard].
- Data Warehousing and Data Mining [3L] Concepts of Data warehousing, data mart, meta data, multidimensional modeling, Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), Online Transaction Processing (OLTP), Data mining concepts, knowledge discovery v. data mining, data mining applications.
7. MS Office Applications [12 P]
MS Excel: Graphs and Charts–Calculation of various financial functions Performing Mathematical Calculations (using Formula and Functions), Searching, Sorting and Filtering, Min Media Mode, Reference Operators, Functions: Typing a Function, Creating a Column Chart: Changing the Size and Position of a Chart Saving
MS Access: Tables and Queries, Forms, Relationship
MS Power Point: Introduction–Toolbar, their Icons and Commands– Navigating in Power point-Creation of slides, animation, and templates-Designing Presentations– Slide show controls–Making notes on Pages and Handouts–Printing Presentations– Customizing Presentations-Auto content Wizard.
Suggested Readings:
- Waman S Jawadekar: Management Information Systems – Text and Cases 3ed. McGraw Hill
- Mahadeo Jaiswal & Monica Mittal: Management Information Systems, OUP
- Forouzan: Data Communication & Networking, TMH.
- Tanenbaum: Computer Networks, Pearson Education
- Ivan Bayross: SQL & PL/SQL, BPB ISRD, Introduction to Database Management Systems, Tata McGraw Hill
- Sadagopan: ERP: A Managerial Perspective, Tata McGraw Hill.
MB – 206: HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
MODULE I
- Human Resource Management: Meaning, Scope, objectives, and functions of HRM
, HR as a Factor of Competitive Advantage, Structure of HR Department, , Line and staff responsibility of HR Managers, Environmental factors influencing HRM (2L)
- Human Resource Planning: definition, objective, process of HRP. Supply and Demand Forecasting techniques, Manpower Inventory, Career Planning& Development, Succession Planning, Rightsizing, Restructuring. Human Resource Information System (HRIS) (6L)
- Recruitment and Selection : Process, Sources, Methods of selection, Interviewing Methods, Skills and Errors. ( 4L)
- Human Resource Development: Definition, objective, process of HRD, Assessment of HRD Needs, HRD Methods: Training and Non-Training, Training Process; Designing, Implementation and Evaluation of Training Programmes, Induction Training. Developing Managerial Skills for: team management, collaboration, interaction across business functions, presentation , Negotiation, and Networking (6L)
- Performance Appraisal Systems : Purpose, Methods, Appraisal instruments, 360 degree Appraisal,HR Score Card, Errors in appraisal, Potential Appraisal, Appraisal Interview. (4L)
MODULE –II
- Compensation Management : Concepts, Components; System of Wage Payment, job evaluation, wage/ salary fixation, incentives, bonus, ESOPs, Fringe Benefits, Retirement Benefits. Compensation Plans (4L)
- Industrial Relations in India: Parties; Management and Trade Unions, Industrial Disputes: Trends, Collective Bargaining, Settlement Machineries, Role of Government, Labour Policy in India. (4L)
- Workers’ Participation in Management: Concept, Practices and Prospects in India, Quality Circles and other Small Group Activities. (2L)
- Discipline Management : Misconduct, Disciplinary action, Domestic Enquiry, Grievance Handling (4L)
- Strategic HRM: Meaning, Strategic HRM vs Traditional HRM, SHRM Process, barriers to SHRM. Nature of e-HRM, eRecruitment & Selection, e-Performance Management, e-Learning (4L)
Suggested Readings:
- Agarwala T. – Strategic Human Resource Management, OUP
- Aswathappa, K. – Human Resource Management, Tata McGraw Hill
- Jyothi P. & Venkatesh, D.N. – Human Resource Management, OUP
- Ramaswamy, E.A. – Managing Human Resources, OUP
- Saiyadain, M.S – Human Resource Management : Tata McGraw Hill
Mondal Sabari & Goswami Amal – Human Resource Management: Vrinda Publications
Third semester and fourth semester papers are not included in the above content.

